Introduction
Note
To find out more about the SPHN Semantic Strategy and the SPHN Ecosystem, watch the seminars on Linked data in SPHN and SPHN Data Ecosystem for FAIR Data
SPHN Semantic Strategy
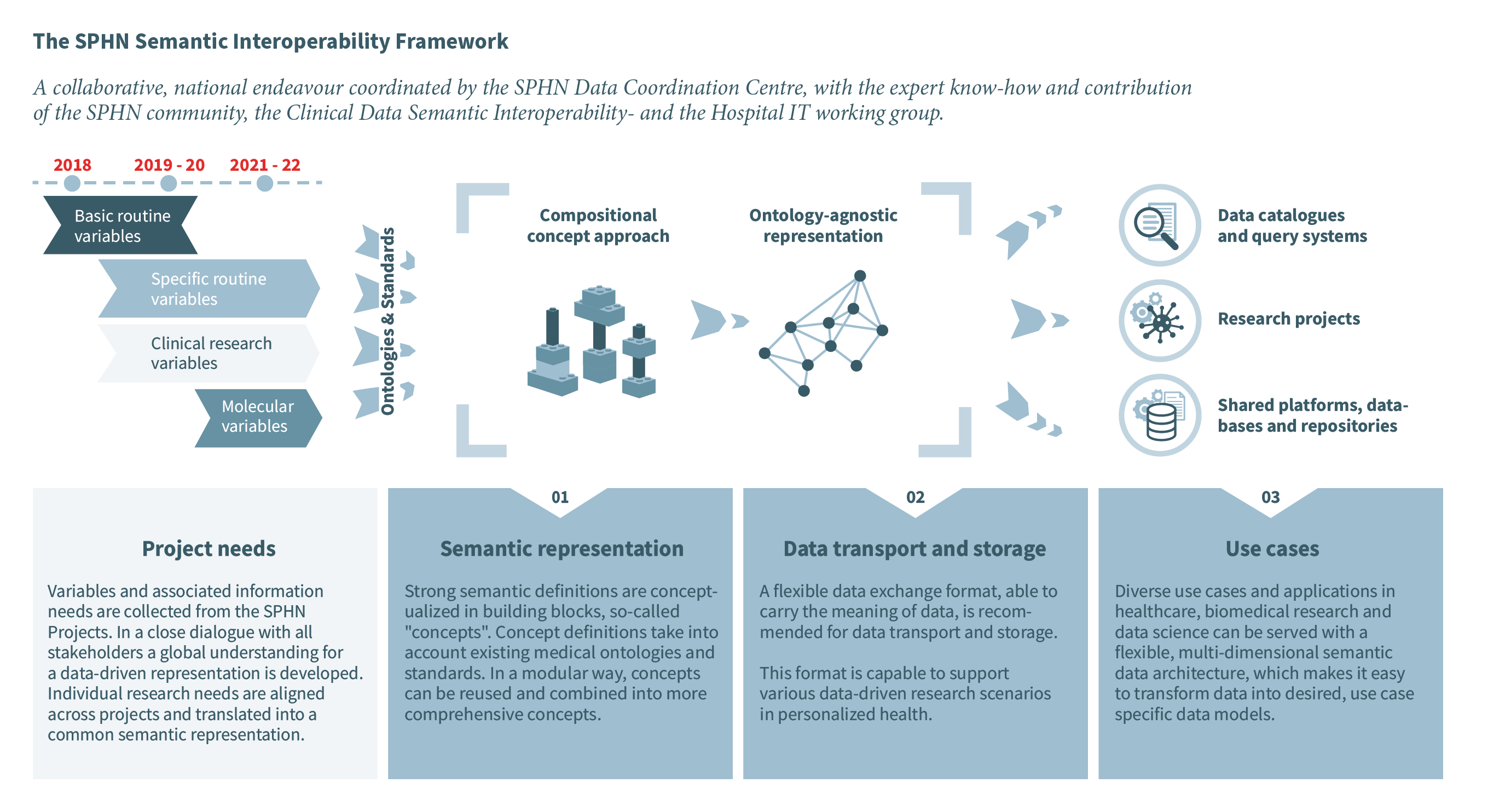
The Swiss Personalised Health Network (SPHN) is an initiative of the Swiss government that aims to provide a framework for exchanging health-related data in an interoperable way for research. Except for some coding systems used for patient billing and accounting, there are currently only a few nationally adopted and implemented standards for medical information in hospitals. To enable the use of health-related data from clinical routine and other sources for research, SPHN has developed a semantic interoperability strategy [Gaudet-Blavignac et al. 2021]. The developed framework is based on the following three pillars strategy:
Pillar 1: Semantic representation,
Pillar 2: Data transport and storage, and
Pillar 3: Use cases.
SPHN Data Ecosystem for FAIR Data
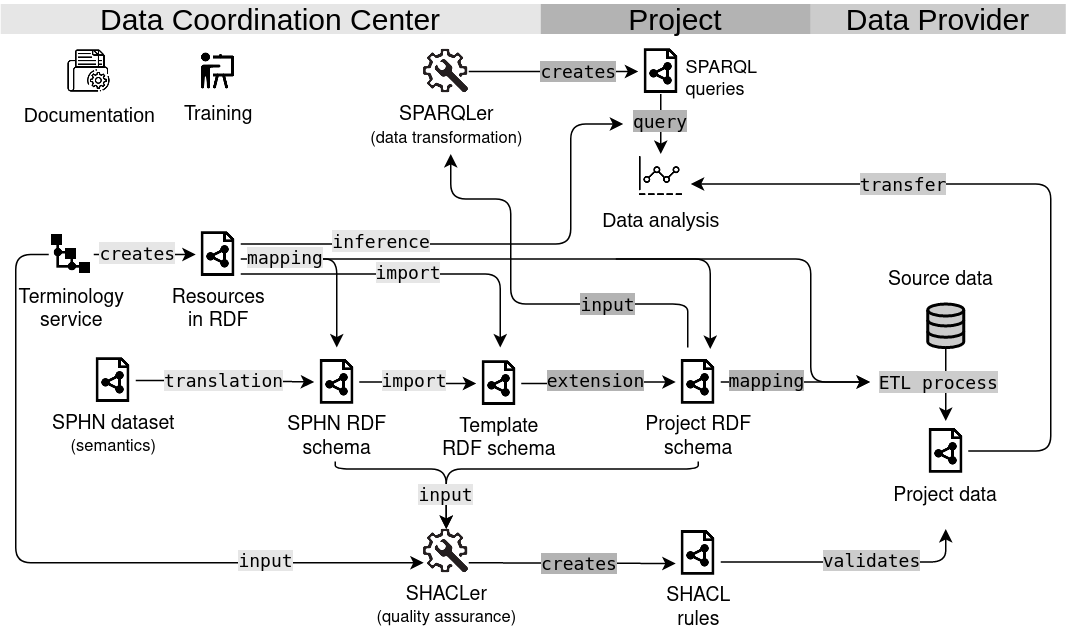
In pursuit of the semantic interoperability strategy, the Data Coordination Center (DCC) has promoted the development of the SPHN Ecosystem [Österle et al. 2021] which encapsulates multiple components. The SPHN Dataset semantically defines medical and health-related concepts used in health research in Switzerland (Pillar 1). The format chosen to enable the storage and exchange of the data is RDF (Resource Description Framework) (Pillar 2). RDF should enable an easier transportation, sharing and use of medical knowledge between hospitals and researchers.
To this end, the SPHN semantics have been incorporated in an SPHN RDF schema that indicates the concepts and rules to follow for generating a structured knowledge graph of the clinical datasets following the FAIR principles. For facilitating the use and integration of external (national and international) standard terminologies and classifications, a Terminology Service [Krauss et al. 2021] has been put in place to automatically transform these content into RDF formats and make them accessible to both data providers and data users who need them at different steps of the presented Ecosystem.
Projects have the possibility to extend the semantics encoded in SPHN to integrate needed information for the project. This extension process is facilitated thanks to the Template RDF schema that can be used as a starting point to extend the SPHN RDF schema into a project-specific RDF schema. The projects send the project-specific RDF schema to the data providers who integrate this schema into their pipelines for transforming clinical data warehouse data and generate RDF data files that complies with the given RDF schema. Data can then be validated with the quality assurance framework mainly composed of the SHACLer and the SPARQLer tools. Once data validated, data users can explore and analyze the data as they need.